Page 11 - hypertension_newsletter6
P. 11
REFLECTIONS
Hypertension
Hypertension Global Newsletter #6 2024
Despite the many achievements in the field, the article concludes with a call for more RCTs on many still incompletely clear or
unaddressed aspects of hypertension. Hypertension
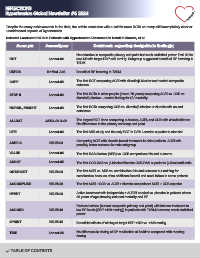
Selected Landmark RCTs in Patients with Hypertension Discussed in Detail in Mancia, et al.
Acronym Journal/year Comments regarding design/main finding(s)
No reduction in composite primary end point but weak statistical power. P=0.05 for
HOT Lancet-98 less MI with target DBP ≤80 mmHg. Subgroup suggested benefit of BP lowering in
T2DM.
UKPDS Br Med J-98 Benefit of BP lowering in T2DM.
CAPP Lancet-98 The first RCT comparing ACEi with diuretic/β-blocker and neutral composite
outcome.
The first RCTs in older people (above 70 years) comparing ACEi vs. CCB vs.
STOP II Lancet-99
diuretic/β-blocker – neutral finding for CV mortality.
The first RCTs comparing CCB vs. diuretic/β-blocker or diuretic with neutral
NORDIL, INSIGHT Lancet-00
outcomes.
The largest RCT done comparing α-blocker, ACEi, and CCB with chlorthalidone:
ALLHAT JAMA-00 &-02
No differences in the primary coronary end point.
LIFE Lancet-02 The first ARB study and the only RCT in LVH: Losartan superior to atenolol.
Comparing ACEi with diuretic-based treatment in older patients. ACEi with
ANBP-2 NEJM-03
possibly better outcome in male subgroup.
VALUE Lancet-04 The first RAS-blocker (ARB) vs. CCB comparison: Neutral outcome.
ASCOT Lancet-05 The first CCB-RAS vs. β-blocker/diuretic: CCB-RAS superior to β-blocker/diuretic.
ONTARGET NEJM-08 The first ACEi vs. ARB vs. combination: Neutral outcome but red flag for
combination because of no additional benefit and renal failure in some patients.
ACCOMPLISH NEJM-08 The first ACEi +CCB vs. ACEi + diuretic comparison: ACEi + CCB superior.
HYVET NEJM-08 Active treatment with indapamide + ACEi if needed vs. placebo in patients above
80 years of age showing reduced mortality and HF.
Reduced stroke (but not composite primary end point) with intense treatment to
ACCORD NEJM-10 low BP levels [SBP <120 mmHg]) in patients with T2DM; however, weak statistical
power.
SPRINT NEJM-15 Beneficial effects of aiming at target SBP <120 vs. <140 mmHg.
TIME Lancet-22 No difference in dosing of BP medication at bedtime compared with morning
dosing.
TABLE OF CONTENTS